Musculoskeletal ultrasound is a great tool in the dynamic evaluation of tendons and ligaments. But the learning curve is real! Let's review common imaging artifacts produced when performing musculoskeletal ultrasound.
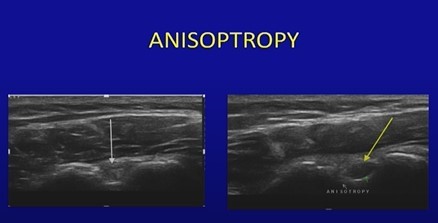
Anisotropy in ultrasound is an angle generated artifact created when the angle of incidence is not perpendicular to the structure which results in a distorted and more hypoechoic (darker) appearance of a nerve, tendon etc. Tilting /angling the transducer to achieve perpendicular incidence to the structure being examined will help to correct this common MSK artifact. Anisotropy may be noted in both long and short axis of tendons and ligaments.
To reduce anisotropic artifact in long axis, the transducer should be angled using the heal-toe maneuver. (See below)
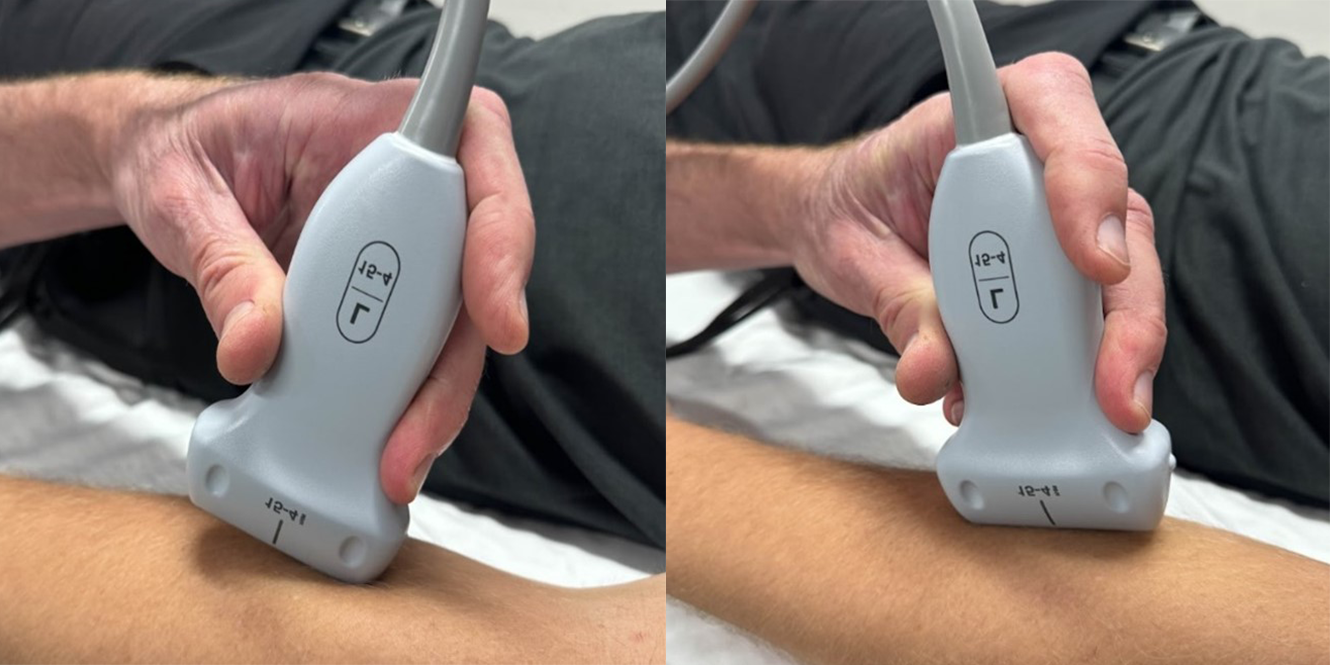
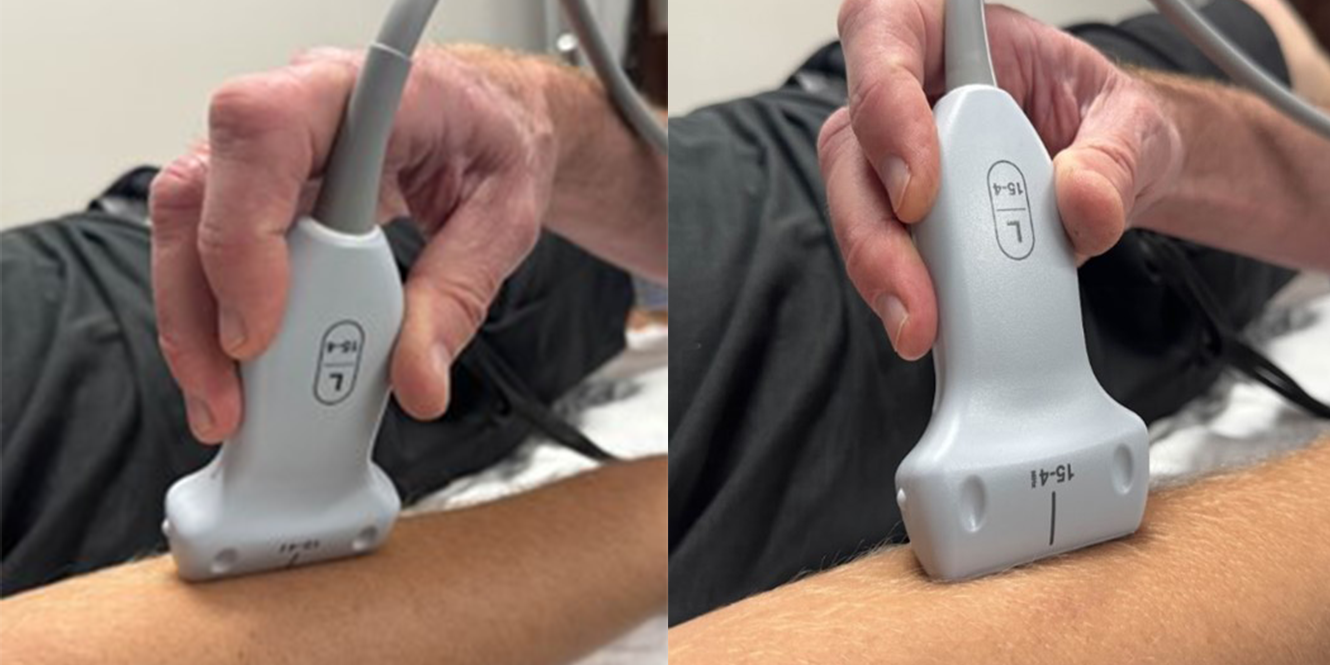
Toggling is another maneuver used to reduce anisotropy. Similar to the heal-toe maneuver, the angle is changed without moving the base to a different location/position. (See below)
Since abnormal tendons and ligaments may appear hypoechoic, it is important to focus on a perpendicular section during the ultrasound examination to exclude anisotropy.
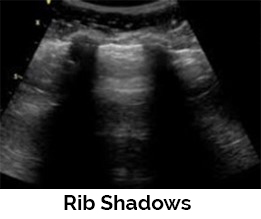
Shadowing artifacts (posterior acoustic shadowing) is caused by the sound wave reflecting back to the transducer or being absorbed by tissue. This artifact occurs as the sound wave interacts with highly reflective structures such as bone, calcifications, or foreign bodies. It is demonstrated by the lack of signal deep to the area imaged. Dirty acoustic shadowing may be observed behind gas bubbles caused by injections.
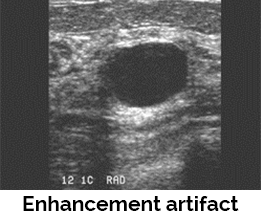
Enhancement artifact - Enhancement (increased through transmission) is seen as echoes that appear brighter than the surrounding tissues posterior to a weakly attenuating structure. Examples of structures that will produce this artifact include a baker cyst, ganglion cyst, or soft tissue abscess. Both shadowing and enhancement can be helpful artifacts for proper diagnosis.
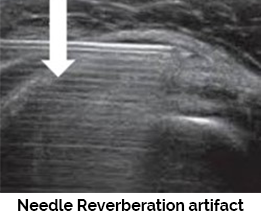
Reverberation artifact - Reverberations appear on the ultrasound display as multiple, equally spaced echoes. Reverberations are formed when a sound wave bounces between 2 strong specular reflectors such as bone and the transducer. Another example of reverberation artifacts is a needle reverberation artifact seen when performing joint aspirations and/or injections.
Refraction artifact - Refraction artifacts take place when a beam strikes an interface that is at an angle (not 90 degrees) and the speed of sound is different at each side of the interface. This artifact can significantly distort and deflect a sound beam causing lateral displacement of a target image.
System optimization is an important first step that will help to minimize these common MSK artifacts.
- Always start with selecting the correct frequency. High frequency = better resolution. Select the highest frequency that allows penetration through area of interest.
- Next, make sure your focal zone is set correctly, which is at the depth of the area being examined. Some systems are electronically focused, so the focal zone may be automatically adjusted. A single focal zone is used when assessment of a specific level is needed, and multiple focal zones can be used when there is a greater range of depth for the area of concern, although using multiple focal zones will diminish the frame rate and may reduce temporal resolution.
References:
Introduction to Musculoskeletal Ultrasound
Dates: August 19th - 21st, 2024
- Most Comprehensive Hands-On Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Course Available
- Introductory MSK US Applications Covered in Depth with Live Scanning Demonstrations for Each Joint
- Upgrade to Include Optional 4-Hour Human Cadaver Workshop (un-embalmed specimens) to Practice Interventional Techniques
- Hands-on Scanning Sessions Feature 3:1 Participant to Expert Faculty Ratio with Standardized Patient Models
- Lifetime Access to Digital Course Materials
- Destination Education in Sunny St. Petersburg, FL
Visit our website or call us for more information:
111 2nd Avenue NE, Suite 800
St. Petersburg, Florida 33701



