A venous duplex ultrasound exam combines a traditional ultrasound, which uses sound waves that bounce off blood vessels to create an image, and Doppler ultrasound, which records sound waves that bounce off moving objects, such as blood, to measure speed and flow.
This procedure is performed to evaluate symptoms including leg pain or swelling, excessive varicose veins, shortness of breath, or suspected blood clots in the legs and/or lungs.
This procedure usually takes place at a Vascular Lab for the venous Doppler/ultrasound duplex exam. The test involves no needles, catheters or dye. Ultrasound is used to listen to the flow of the blood through your veins.
The person receiving the exam will be asked to lie still on a table with their head slightly elevated. The medical professional administering the exam will apply a gel to the area of the body being examined. A transducer (ultrasound probe) is then moved gently over the area being tested. The exam usually only takes approximately 30 minutes to complete.
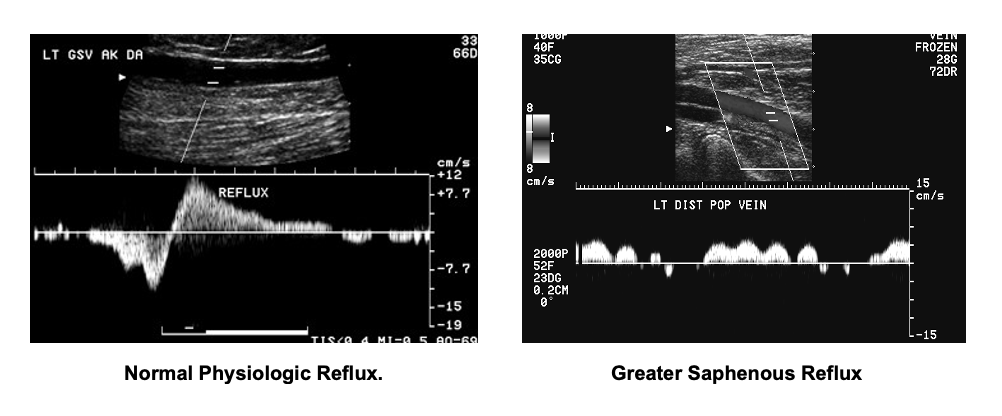
Venous insufficiency occurs when legs do not allow a steady flow of blood back to the heart. Venous duplex imaging provides information about valve function and the levels of involvement. The duration of reflux is known as “reflux time”. A reflux time of >0.5 seconds for superficial (greater saphenous and small saphenous) and >1.0 seconds for deep veins is used to diagnose the presence of reflux. Typically, the longer the duration of reflux time implies more significant disease. These exams are usually performed in a standing position.
Risk factors for venous insufficiency include:
- Being overweight
- Pregnancy
- Family history of venous disease
- Previous history of deep vein thrombosis