Prehospital ultrasound is an exciting field with many diagnostic applications that can aid in early diagnosis and determine the management and possibly the destination of a patient with minimal time delays. Our military field/combat medics may be required to move quickly, and POCUS provides a faster and more efficient way to streamline care.
A few of the current applications of EMS / Prehospital ultrasound include:
• Trauma / EFAST Exam for detection of intraperitoneal hemorrhage (also useful for suspected ruptured ectopic pregnancy), pericardial fluid / tamponade, and hemothorax/pneumothorax. Lightweight handheld ultrasound systems can reliably detect between 200-650ml of free fluid in the abdomen and can identify as little as 20ml of fluid in the pleural space. The EFAST exam can be completed by the experienced EMS provider in as little as 2 minutes.
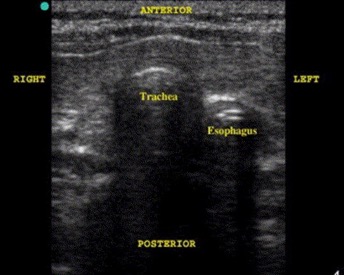
• Endotracheal Tube Placement. Ultrasonography is increasingly being used to confirm the correct placement of ETT. Tracheal intubation is confirmed if only one air-mucosal interface with posterior shadowing and reverberation artifact is visualized. Esophageal intubation is suspected if two air-mucosal interfaces with shadowing were noted (double tract sign.
• Central and peripheral venous access. Real-time ultrasound guidance increases the rate of success.
• Cardiac.ultrasound for contractility/function, pericardial effusion, and resuscitation evaluation.
• Thoracic ultrasound for the diagnosis of pneumothorax. Pulmonary edema, pleural effusion, and lung consolidation are other common applications when performing thoracic ultrasound. B-Lines (comet tail artifact) are hyperechoic vertical lines imaged on chest ultrasound. One or two B- Lines is normal. Multiple B-lines may indicate pulmonary edema.
•Ocular. (typically performed in the emergency department) ultrasound can assist in the diagnosis of globe rupture, vitreous hemorrhage, retinal detachments, foreign bodies, and ocular infections. The fluid filled eye makes it the perfect organ for imaging. Optic nerve sheath measures can be obtained with head injury / suspected elevated intracranial pressure.
The use of POCUS WILL continue to expand. A few of the other applications include musculoskeletal / soft tissue imaging and procedural guidance when performing nerve blocks.
In the past the 2 largest drawbacks to portable ultrasound were:
1. Cost.
Smaller lightweight handheld systems are now more affordable.
2. Proper training was difficult to obtain.
Gulfcoast Ultrasound offers LIVE, BLENDED, and CUSTOM courses for all your EMS / POCUS needs.