Transcranial Doppler is a non-invasive technique for evaluating blood flow information from the intracranial arteries located at the base of the brain.
Transcranial techniques were initially described by Rune Aaslid in 1982. The equipment and technology have since progressed to involve numerous clinical and research applications.
The clinical applications of TCD include:
- Detecting severe stenosis in the major intracranial vessels.
- Assessment of patterns and extent of collateral circulation with known regions of severe stenosis or occlusion.
- Detection of arteriovenous malformations and supplying arteries.
- Evaluation and follow-up with vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Assessment of patients with suspicion of brain death.
- Screening for stenosis in pediatric patients with Sickle Cell Disease.
Indications for requesting a TCD exam include:
- Patients symptomatic for cerebrovascular disease.
- Patients with known cerebrovascular disease greater than 80% diameter reduction.
- Patients with normal carotid duplex exams with persistent TIA’s.
- Patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage who are at risk for vasospasm.
- Patient with head trauma who may need evaluation for hyperdynamic flow.
Technique
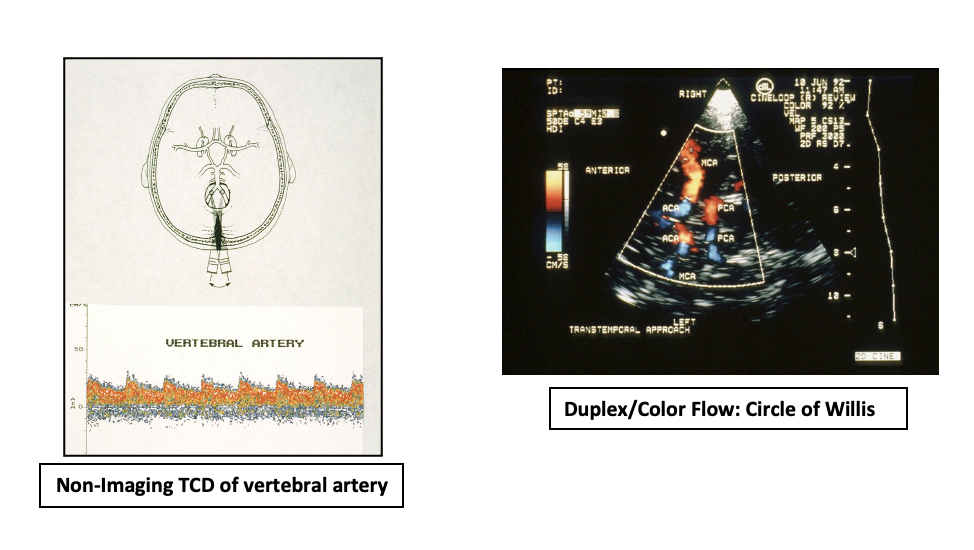
Transcranial Doppler techniques can be performed with a non-imaging 1-3 MHz pulsed Doppler instrument with flow information displayed by a real time spectrum analyzer and/or by using Duplex/color Doppler imaging.
The cerebrovascular anatomy evaluated by transcranial Doppler techniques involves the anterior circulation, posterior circulation, siphon, and genu. Four primary acoustic windows are used to evaluate the various intracranial vessels. These include:
- Transtemporal
- Suboccipital
- Transorbital
- Submandibular
Transcranial Ultrasound may also be used as a resource for monitoring micro-emboli during surgery and also monitoring of treatment efficacy.
Transcranial ultrasound can offer a multi-modality capability to evaluate the brain structure and vasculature. It offers portable, highly reliable, and reproducible techniques that support various therapeutic decisions and serves as a monitoring tool during surgical or neurointerventional procedures.
Successful integration of transcranial ultrasound requires sufficient knowledge and hands-on skills training to develop the technical expertise to accurately perform and/or interpret the examinations.