What is Adult Echocardiography (Cardiac Ultrasound)?
Adult echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is a non-invasive imaging technique used to assess the structure and function of the heart. It utilizes high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to create detailed images of the heart’s chambers, valves, walls, and blood vessels in real-time. Echocardiography plays a critical role in diagnosing, monitoring, and managing a variety of cardiovascular conditions. The actual examination performed for diagnostic purposes is known as an echocardiogram.
Why Is a Cardiac Ultrasound Important?
A cardiac ultrasound plays a critical role in the early detection, diagnosis, and monitoring of heart diseases. It helps physicians:
- Determine the cause of chest pain, shortness of breath, or fatigue.
- Guide treatment decisions for valvular heart disease, heart failure, and congenital defects.
- Monitor heart function after a heart attack or cardiac surgery.
- Evaluate whether medical interventions or medications are improving heart function.
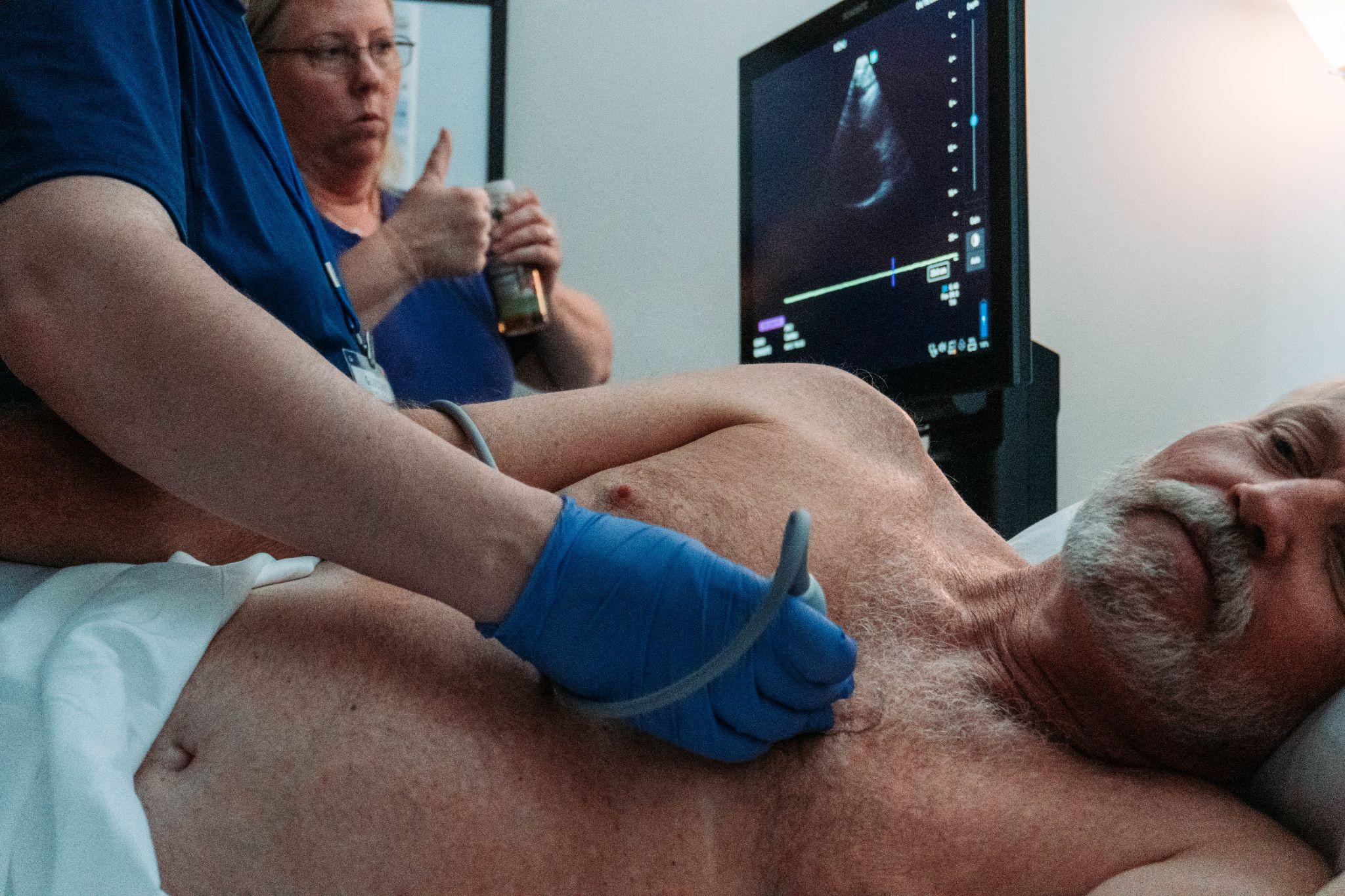
Who performs echocardiography?
Echocardiography is typically performed by highly trained healthcare professionals specializing in cardiac imaging. Depending on the setting and type of echocardiogram, the following individuals may be involved:
Cardiac Sonographers (Echocardiographers)
Cardiac sonographers - also known as echocardiographers - are specialists trained in using ultrasound equipment to perform echocardiograms. They have expertise in:
- Operating the ultrasound machine to capture high-quality heart images.
- Recognizing normal and abnormal heart structures and functions.
- Collaborating with physicians to provide preliminary findings that guide diagnosis.
Most cardiac sonographers hold certifications from professional bodies such as:
- ARDMS (American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography) – Certification in Adult Echocardiography
- CCI (Cardiovascular Credentialing International) – Registered Cardiac Sonographer (RCS)
Cardiologists
Cardiologists, particularly those specializing in non-invasive cardiology, often interpret echocardiograms. While sonographers perform the imaging, cardiologists provide the final diagnosis based on the findings. Cardiologists also perform specialized echocardiograms such as:
- Transesophageal echocardiograms (TEE)
- Stress echocardiograms during or after exercise testing
In some cases, cardiologists perform echocardiograms themselves in critical situations where immediate results are needed, such as in emergency rooms or during invasive procedures.
Anesthesiologists and Intensivists
In specialized settings, anesthesiologists and critical care physicians (intensivists) may perform or oversee transthoracic (TTE) or transesophageal echocardiograms (TEE). This is particularly common:
- During cardiac surgeries to monitor heart function in real-time
- In ICUs to assess heart performance in critically ill patients
- In emergency situations where point-of-care cardiac evaluation is required
Emergency Medicine Physicians
In emergency departments (EDs), physicians trained in point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) use focused echocardiography to assess cardiac function quickly. This may be performed to:
- Identify pericardial effusion or tamponade
- Detect signs of heart failure or cardiac arrest
- Guide resuscitative efforts
Primary Care and Internal Medicine Physicians
With advancements in portable ultrasound technology, primary care doctors, advanced level practitioners such as physician assistants (PA’s) and Nurse Practitioners (NP’s), and internists are increasingly using focused echocardiography in outpatient settings to detect heart conditions early and refer patients to specialists for further evaluation.
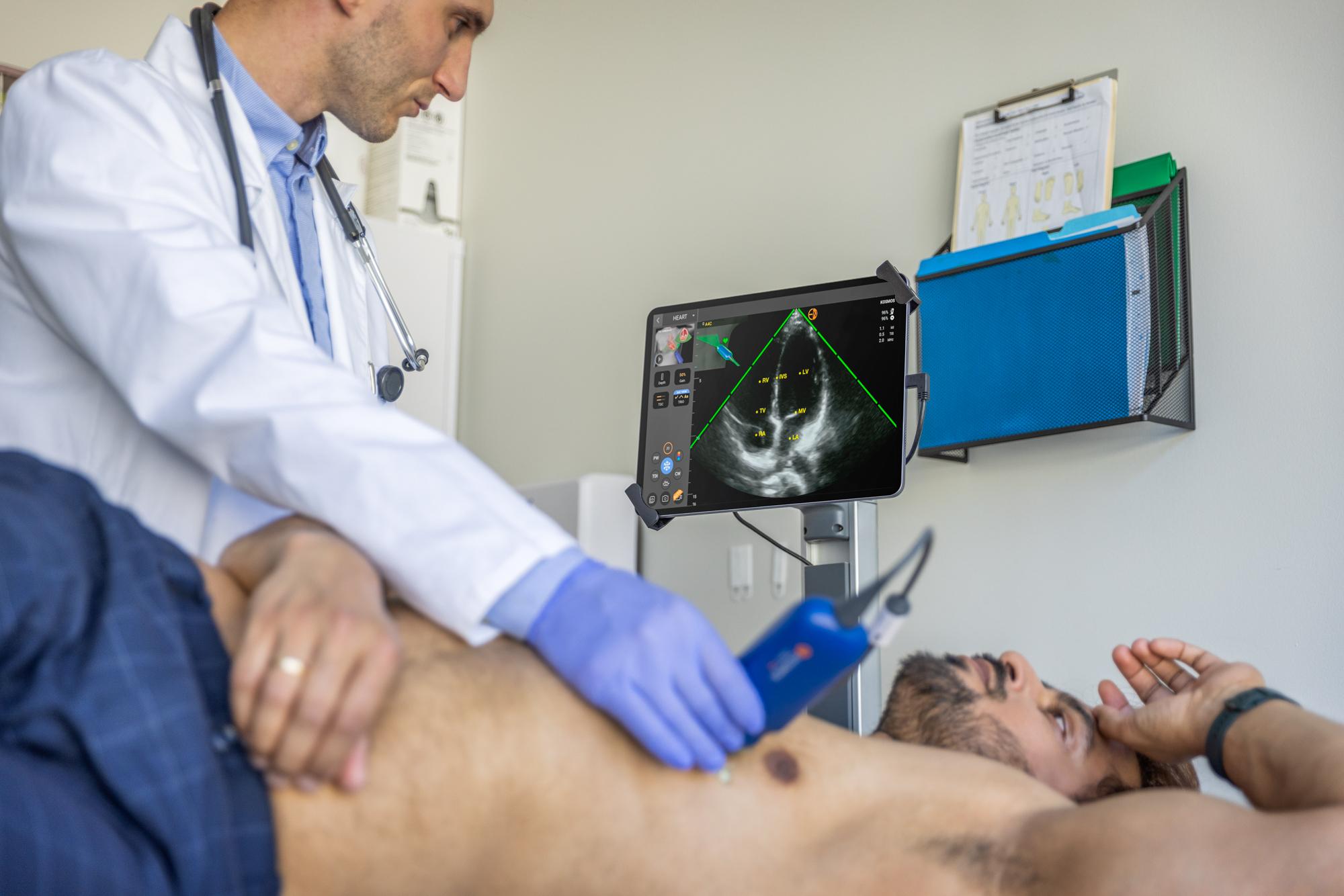
What are the different types of echocardiography exams?
- Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE): The most common type, performed by placing the transducer on the patient’s chest using a Phased Array transducer.
- Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE): A more detailed test, where a probe is inserted into the esophagus to capture closer, clearer images of the heart structures.
- Stress Echocardiogram: Conducted while the heart is under stress (through exercise or medication) to evaluate how well the heart performs under increased workload.
- Doppler Echocardiogram: Focuses on the movement of blood through the heart, identifying abnormal flow patterns or blockages.
What’s the difference between an echocardiogram and an EKG?
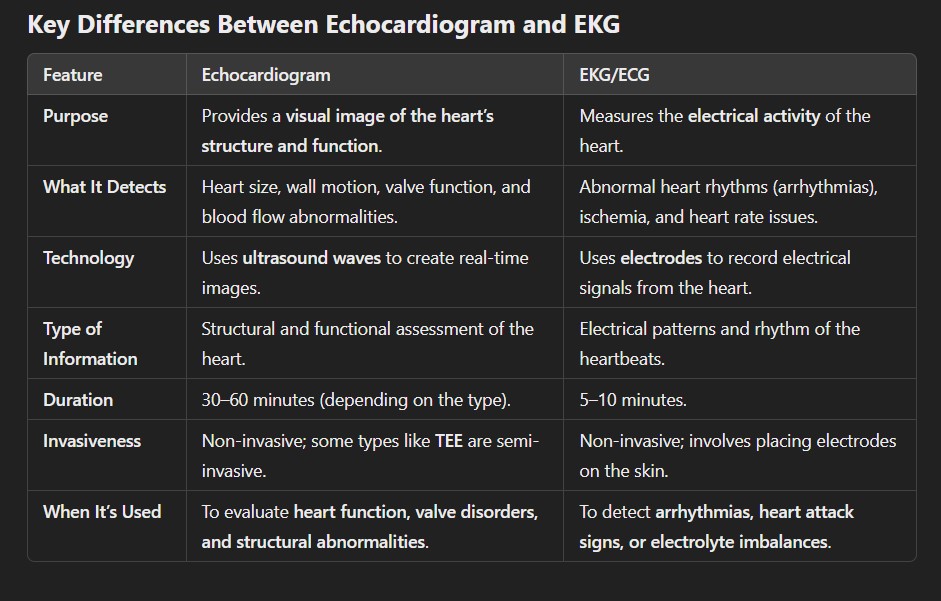
When to Use an Echocardiogram vs. an EKG
Echocardiogram
- Used when physicians need a detailed picture of the heart’s anatomy.
- Helps diagnose conditions like heart valve disease, cardiomyopathy, congenital defects, heart failure, and more
- Also monitors blood flow through Doppler imaging, offering insight into how well the heart is pumping and if there are blockages or valve issues.
EKG/ECG
- Often the first test is ordered for patients experiencing chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, or dizziness.
- Detects irregular heart rhythms (like atrial fibrillation) and signs of ischemia or past heart attacks.
- Frequently used for monitoring cardiac health during routine physical exams or before surgeries.
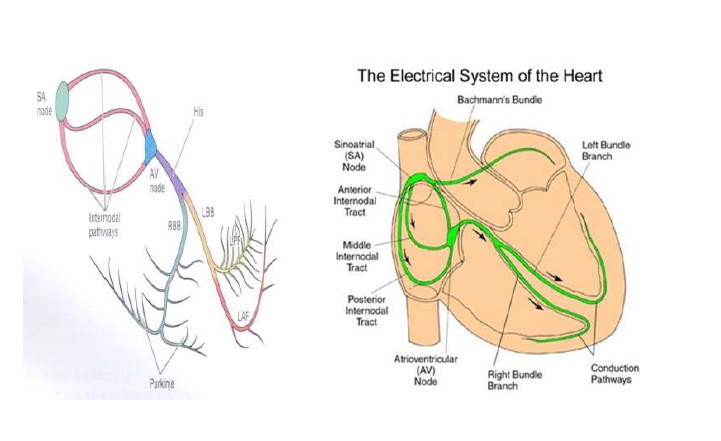
Complementary Use of Echocardiogram and EKG
In many cases, echocardiograms and EKGs are used together to provide a comprehensive assessment of heart health. For example:
- An EKG might detect an abnormal rhythm, prompting further investigation with an echocardiogram to see if there is an underlying structural problem.
- If an echocardiogram shows reduced heart function, an EKG might be ordered to check for rhythm disturbances that could explain the dysfunction.
What techniques are used in echocardiography
Echocardiography employs several specialized techniques to provide comprehensive views of the heart’s structure and function. Each technique serves a distinct purpose, helping healthcare providers diagnose and monitor cardiovascular conditions with precision.
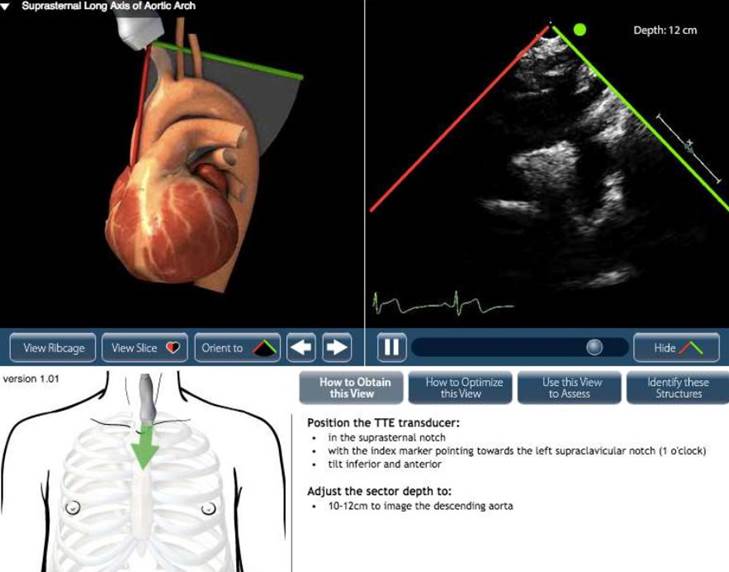
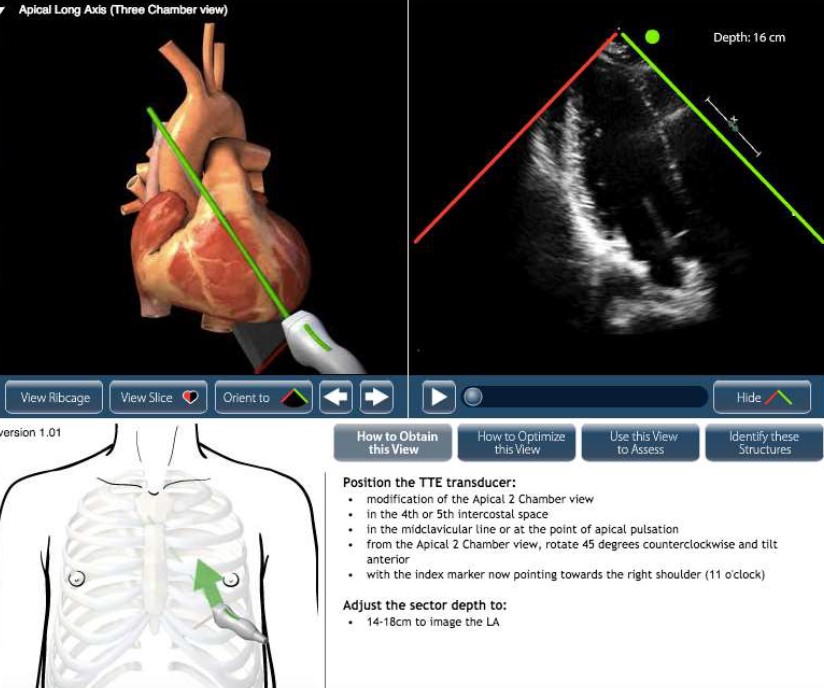
Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
The most common and non-invasive echocardiography technique, TTE involves placing a transducer on the chest wall to obtain images of the heart through the ribs and chest tissue.
Used for:
- Assessing heart size, wall motion, and pumping function
- Evaluating heart valves for stenosis or regurgitation
- Identifying fluid around the heart (pericardial effusion)
Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE)
TEE provides more detailed images by inserting a specialized probe into the esophagus, placing the transducer closer to the heart without interference from bones or lungs.
Used for:
- Detecting small clots, tumors, or infections (endocarditis)
- Monitoring the heart during cardiac surgeries or catheter-based procedures
- Evaluating prosthetic heart valves and congenital heart defects
Stress Echocardiography
This technique assesses how well the heart functions under stress, either through exercise (treadmill or bike) or pharmacologic agents (such as dobutamine).
Used for:
- Detecting coronary artery disease
- Assessing heart performance under increased workload
- Identifying areas of the heart with poor blood flow (ischemia)
Doppler Echocardiography
Doppler imaging measures the speed and direction of blood flow through the heart’s chambers and valves. It is essential for evaluating heart function and identifying blood flow abnormalities.
Used for:
- Detecting valve stenosis (narrowing) or regurgitation (leakage)
- Measuring intracardiac pressures and cardiac output
- Identifying abnormal connections (such as shunts)
Color Doppler Imaging
A variation of Doppler echocardiography, Color Doppler uses color maps to represent blood flow direction and velocity.
Used for:
- Visualizing turbulent blood flow due to valve dysfunction
- Detecting leaks in heart valves or abnormal blood flow patterns
- Assessing blood flow in congenital heart defects
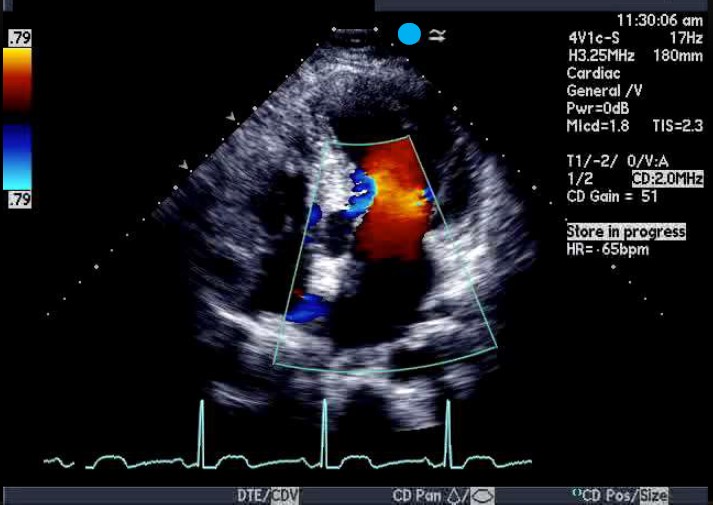
3D Echocardiography
This technique provides three-dimensional images of the heart, allowing for detailed assessment of complex cardiac structures.
Used for:
- Evaluating valve morphology before and after repair
- Assessing congenital heart defects
- Enhancing visualization during interventional procedures like TAVR
Contrast Echocardiography
In contrast echocardiography, a contrast agent (microbubbles) is injected into the bloodstream to enhance the visualization of the heart’s chambers and walls.
Used for:
- Evaluate overall cardiac function
- Detecting shunts or abnormal blood flow between heart chambers
- Enhancing endocardial border definition in patients with suboptimal images
- Assessing myocardial perfusion in ischemic heart disease
Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS)
POCUS is a focused, bedside echocardiographic technique used in emergency and critical care settings for rapid evaluation of heart function.
Used for:
- Detecting pericardial effusion or tamponade
- Assessing heart function during cardiac arrest
- Guiding fluid resuscitation and hemodynamic monitoring
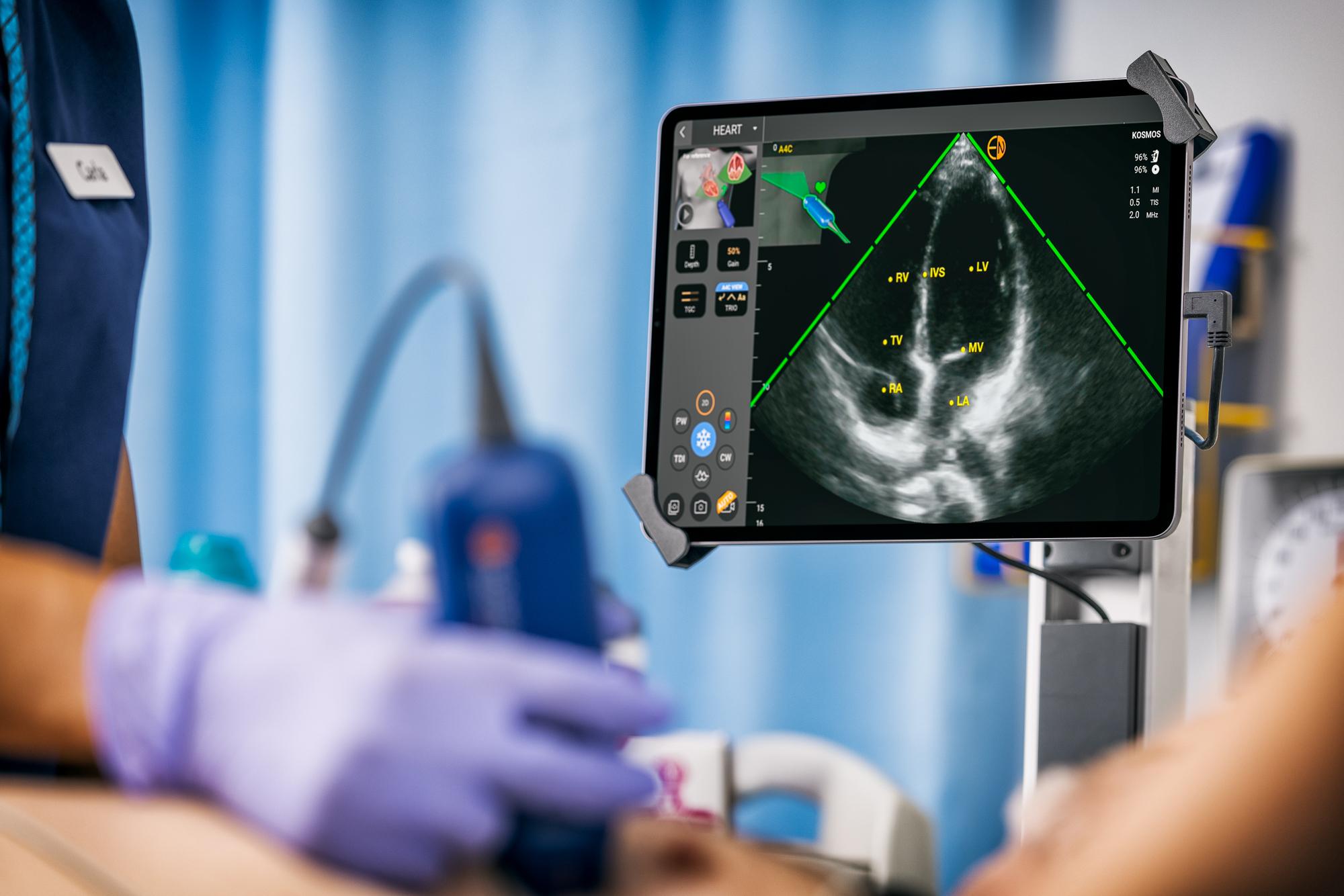
What does a cardiac ultrasound show?
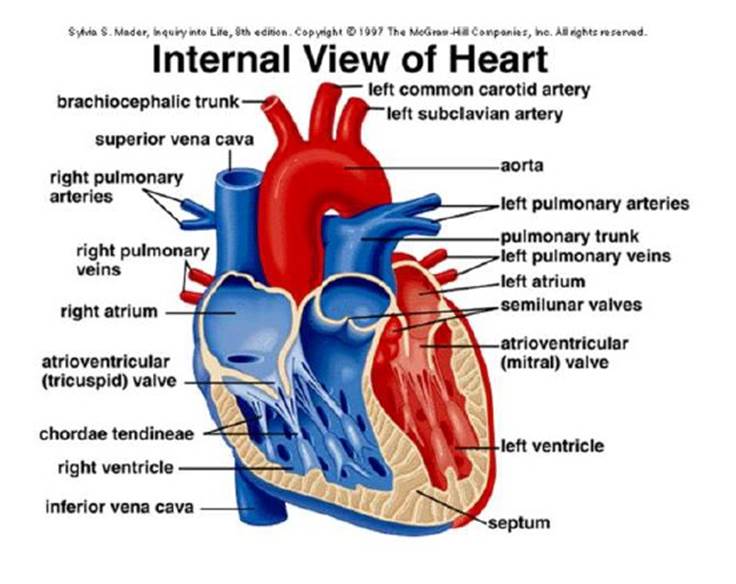
Heart Chambers and Wall Motion
- Chamber Size and Shape: Detects enlargement or shrinkage of the atria and ventricles.
- Wall Motion Abnormalities: Identifies areas of the heart muscle (myocardium) that aren’t contracting properly, which may indicate ischemia or heart attack damage.
- Ejection Fraction (EF): Measures the percentage of blood the left ventricle pumps out, helping to diagnose heart failure.
Heart Valves
- Valve Function: Determines if valves open and close properly.
- Valve Stenosis: Identifies narrowing of valves, such as in aortic stenosis.
- Valve Regurgitation: Detects leaky valves that allow blood to flow backward, causing conditions like mitral regurgitation.
- Prosthetic Valve Evaluation: Monitors the performance of artificial or repaired valves.
Blood Flow and Pressure
- Doppler Imaging: Measures the speed and direction of blood flow through the heart’s chambers and valves.
- Pulmonary Artery Pressure: Helps diagnose pulmonary hypertension by estimating the pressure in the pulmonary arteries.
- Shunts and Abnormal Flow Patterns: Detects congenital heart defects, such as atrial or ventricular septal defects, where blood flows between chambers abnormally.
Pericardium (Heart Lining)
- Pericardial Effusion: Detects fluid accumulation around the heart, which may indicate infection, inflammation, or cancer.
- Cardiac Tamponade: Assesses whether fluid buildup is compressing the heart, impairing its ability to pump effectively.
Congenital Heart Defects
- Identifies structural abnormalities present from birth, such as septal defects (holes in the heart) or abnormal valve structures.
- Monitors the success of surgeries or interventions used to correct congenital defects.
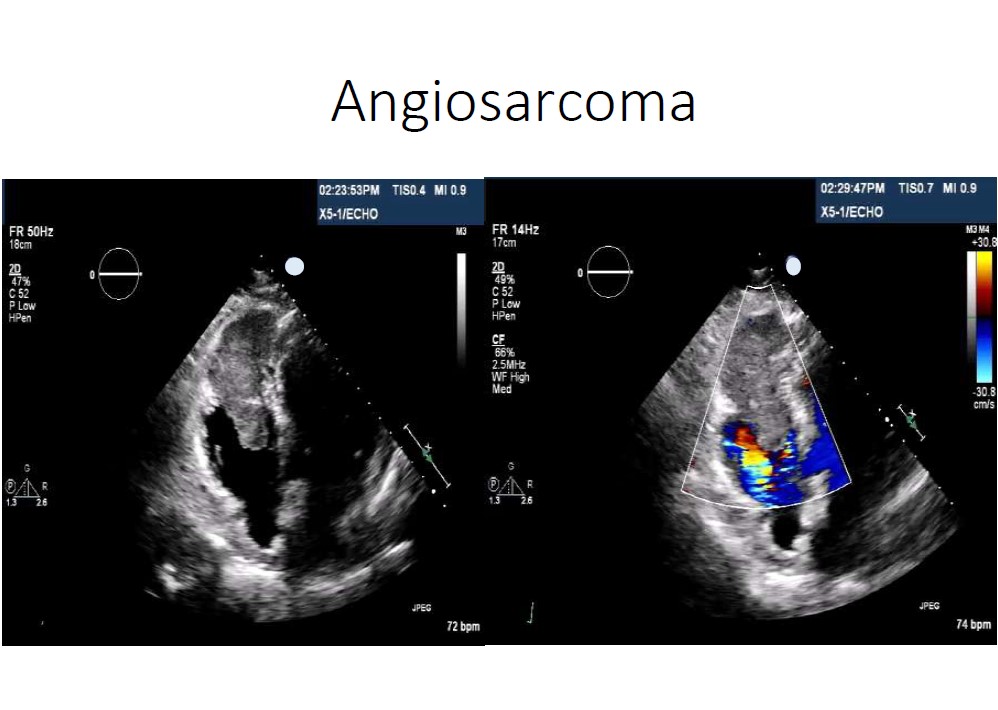
Cardiac Masses or Clots
Blood Clots (Thrombi): Finds clots that may form inside the heart, often in patients with atrial fibrillation or weakened heart function.
Tumors or Growths: Detects cardiac tumors like myxomas or other abnormal masses within the heart chambers.
What Ultrasound Equipment is needed for echocardiography?
Performing echocardiography requires specialized ultrasound equipment designed to capture high-resolution images of the heart’s structures and monitor its function in real time. Below is a breakdown of the key equipment and components needed for a complete echocardiographic evaluation.

Ultrasound Machine
A high-performance ultrasound system is essential for echocardiography to ensure clear and accurate images. Key features of a cardiac ultrasound machine include:
- Sector phased array transducers for precise imaging.
- Advanced Doppler modes (Color, Pulsed, and Continuous Wave Doppler) for evaluating blood flow and valve function.
- 3D/4D capabilities for real-time, volumetric heart imaging.
- Stress echocardiography support to assess cardiac performance during physical or pharmacologic stress tests.
- TEE compatibility for transesophageal echocardiography procedures.
Transducers (Probes)
Echocardiography relies on multiple specialized probes to capture different views of the heart. Common types include:
- Transthoracic Transducer (TTE Probe): A phased-array transducer for imaging through the chest wall.
- Transesophageal Probe (TEE Probe): A long, flexible probe inserted into the esophagus to obtain clearer images of the heart’s posterior structures.
- Pedoff Probe (Continuous Wave Doppler): A pencil probe used for measuring high-velocity blood flow across valves.
- High-frequency Transducer: Used for pediatric applications.
Doppler Imaging Capabilities
Doppler ultrasound modes are crucial for evaluating blood flow and valve function. A cardiac ultrasound machine must include:
- Color Doppler: Visualizes blood flow patterns and turbulence.
- Pulsed Wave Doppler: Measures blood flow at a specific location.
- Continuous Wave Doppler: Captures high-velocity blood flow, often used to assess valve stenosis or regurgitation.
ECG Monitoring System
A built-in ECG (electrocardiogram) monitor is often integrated into ultrasound machines. This allows the ultrasound system to synchronize heart images with the patient’s cardiac cycle, ensuring accurate timing for measurements like ejection fraction and valve function.
Image Storage and Reporting Software
Modern echocardiography systems must support image storage, review, and reporting. Key features include:
- DICOM compatibility for seamless integration with PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems).
- Automated measurements and reporting tools to generate quick, standardized reports.
- Cloud storage or local servers to archive patient studies.
Stress Test Equipment (for Stress Echocardiography)
When performing stress echocardiograms, the following additional equipment is required:
- Treadmill or stationary bike for exercise-induced stress tests.
- Pharmacologic agents like dobutamine, when physical stress tests are not possible.
- Vital sign monitoring systems to ensure patient safety during stress tests.
Contrast Agents (for Contrast Echocardiography)
In some cases, Echo-enhancing imaging agents (previously referred to as contrast agents) are used to enhance image quality. These agents improve visualization of:
- Left ventricular walls and endocardial borders.
- Intracardiac shunts and abnormal blood flow patterns.
How to become a registered echocardiographer
Becoming certified in echocardiography as a sonographer involves a combination of formal education, clinical training, and passing certification exams. Certification demonstrates your proficiency in performing and interpreting cardiac ultrasound, ensuring high-quality care, and improving job prospects. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to become certified in echocardiography. Here is a Guide created by Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute.

Complete the Required Education
Earn a Degree or Certificate in Diagnostic Medical Sonography
Enroll in a cardiovascular sonography program or a general diagnostic medical sonography program with a concentration in echocardiography.
- Associate’s or bachelor’s degree programs are common paths.
- Accredited programs ensure eligibility for certification exams (look for CAAHEP-accredited programs).
Alternative Path
Some healthcare professionals (that already have an allied health degree) may enter echocardiography through specialized ultrasound training programs or continuing education courses such as those offered by Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. (make sure to look for programs accredited by the ACCME)
Gain Clinical Experience
Many sonography programs include clinical rotations or internships to provide hands-on training under the supervision of experienced echocardiographers.
You will need documented clinical experience to meet the requirements of most certifying bodies, such as the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) or Cardiovascular Credentialing International (CCI).
Choose the Right Certification Path
There are two primary certification organizations for echocardiography in the United States, Both their credentials (RDCS and RCS) are widely recognized and respected in the field.
ARDMS (American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography)
Credential: Registered Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographer (RDCS)
Specialties:
- Adult Echocardiography (AE)
- Pediatric Echocardiography (PE)
- Fetal Echocardiography (FE)
Requirements:
- Completion of a sonography program or relevant allied healthcare degree
- Documented clinical experience
- Passing the Sonography Principles and Instrumentation (SPI) exam and a specialty exam (such as AE for adult echocardiography).
CCI (Cardiovascular Credentialing International)
Credential: Registered Cardiac Sonographer (RCS)
Requirements:
- Completion of a cardiac ultrasound or sonography program
- Clinical experience verified by an employer or preceptor
- Passing the RCS exam
Pass the Required Certification Exams
SPI Exam (Sonography Principles and Instrumentation):
- Covers ultrasound physics and instrumentation.
- Required for ARDMS certification (you only need to pass it once, even if pursuing multiple specialties).
Specialty Exams:
- Adult Echocardiography (AE): Focuses on performing and interpreting echocardiograms for adult patients.
- Pediatric Echocardiography (PE): Covers imaging techniques specific to children’s hearts.
- Fetal Echocardiography (FE): Focuses on prenatal cardiac imaging.
For the RCS credential (CCI), you’ll take a comprehensive exam covering echocardiography techniques and cardiac pathology.
Maintain Certification Through Continuing Education
Both ARDMS and CCI require sonographers to maintain certification by earning continuing medical education (CME) credits.
CME activities ensure you stay updated on the latest advancements in echocardiography and sonographic practices.
At Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute, we offer CME courses designed to meet recertification requirements for RDCS and RCS professionals.
Take Your Echocardiography Skills to the Next Level with Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute
Whether you’re preparing for certification, expanding your POCUS skills, or learning echocardiography for the first time, Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute provides comprehensive training designed for sonographers, physicians, and advanced-level providers. Our expert-led workshops, online CME courses, and registry exam preparation materials ensure you gain the practical skills needed to improve diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes while taking your career to the next level.
Register Today!
Online Echocardiography Courses
Echocardiography Training Videos
Echocardiography Exam Preparation Materials

